Time and Time Zones
Days and nights occur because the earth spins on an axis. The sun illuminates approximately half of the earth’s surface, but since the earth is constantly turning, we divide the earth into twenty-four time zones; one for each hour of the day. Some time zone boundaries zigzag so that people living in one region or country can have the same time.
Until the nineteenth century, each city kept local time. Clocks were not often very accurate, but they could be synchronized, or matched, with a sundial. Railroad engineers created the first time zones in Great Britain. A railroad would use the same tracks to send trains in different directions so an inaccurate clock could cause a disaster. A Canadian named Sanford Fleming first proposed the idea of universal time zones; by 1900, most nations began to use what became known as “standard time.”
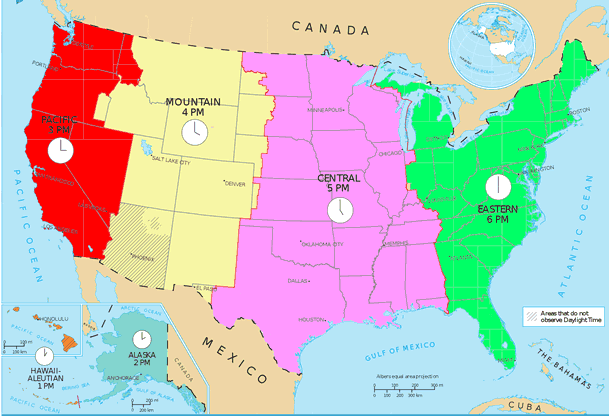
The time along the prime meridian in Greenwich, England, is known as Greenwich Mean Time, or GMT. People communicating across two different parts of the globe often use Greenwich Mean Time. The east coast of the United States is five time zones behind GMT, so if it is midnight in Greenwich it is 7:00 p.m. in Florida. Most of the United States sets their clocks ahead one hour in the summer, so during Daylight Saving Time the east coast of the United States is four hours behind Greenwich Mean Time.
There are four time zones in the continental United States. The continental United States refers to the forty-eight contiguous states and does not include Alaska or Hawaii. The time zones are Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific. You might notice that live television programs often begin at 8:00 Eastern, 7:00 Central, 6:00 Mountain and 5:00 Pacific. Alaska is an hour behind Pacific Time and Hawaii is two hours behind Pacific Time.
For convenience, almost all of Alaska uses a single time zone. During the period when Daylight Saving Time is not in use, the sun is overhead at about noon in Alaska’s capital, Juneau. Juneau is in the eastern portion of Alaska. Nome is in western Alaska, and while Nome has the same time zone as Juneau, the sun is directly overhead as late as 3:08 p.m.
Resources
Download this lesson as Microsoft Word file or as an Adobe Acrobat file.
Listen to the lesson read by Paul Christopher. (mp3)
Lexile® Measure 1060L
Mr. Donn has an excellent website that includes a section on Geography.
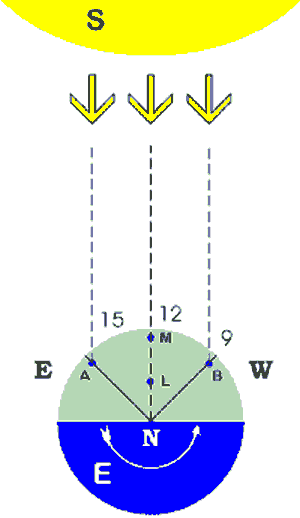
Days and nights occur because the earth spins on an axis.